Table Of Contents
Did you know that Nigeria is home to more than 250 fintech companies? With this large number of firms in the financial services industry, it is no surprise that digital identity verification has become a key sector in the Nigerian economy. Since most fintechs need a comprehensive method to verify user identities, the identity verification industry has also seen major growth in the west African country.
Along with rapid growth in the financial services industry, Nigeria has also seen a massive increase in financial and cybercrimes in the past few years. Studies disclose that a whopping $18 billion is lost to financial crimes like bribery and internet fraud in the country every year. Though Nigerian regulatory bodies have introduced numerous laws to combat financial crimes, the advancement of technology has made it somewhat easier for fraudsters.
Identifying users via KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures plays a key role in protecting the financial industry in Nigeria, so let’s understand the key steps of identity verification in the country.
Who regulates the financial industry in Nigeria?
The Central Bank of Nigeria regulates and supervises the financial institutions in Nigeria, under the guidelines of FATF (Financial Action Task Force), GIABA (Inter-Governmental Action Group against Money Laundering) and the OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control). These financial institutions include all types of banks, finance houses and holding companies.
How can customer identity be verified?
The steps involved in identity verification in Nigeria include
1. Identifying the customer:
a. Financial institutions first have to establish the identity of their prospective customers, ensuring that the customer is actually the person they are claiming to be.
b. If a financial service is being used by someone on behalf of another individual, both their identities must be verified.
2. Screening the customer
This includes evaluating the risk profile of users from their past financial behaviour.
The user is then screened against sanctions, PEPs and adverse media lists (depending on their risk assessments).
3. Enhanced due diligence
For high-risk customers more detailed information about their financial history along with greater checks has to be carried out.
Nigeria’s National Identity Database
The NIMC (National Identity Management Commission) issues and regulates identity documents in Nigeria, including NIN (National Identification Number) enrollment, National ID issuance, identity verification and authentication.
The NIN is used to link citizens’ and legal residents’ biometric data to the National Identity database, which is then used for verification and authentication. Used for identification purposes for all transactions based in Nigeria, the National ID card can be used as
1. An identity card
2. An electronic ID for KYC
3. A biometrics ID (using fingerprints)

Some identity documents that can be used in Nigeria to validate a user’s identity are:
- NIN card
- Passport
- Birth certificate
- Driver’s license
NIMC’s mobile ID app has a feature called virtual NIN. This virtual NIN is a tokenised version of an individual’s actual NIN and can be used for digitally verifying a user’s identity before offering a service.
The virtual NIN is a token consisting of 16-digit alphanumeric characters and expires 72 hours after being generated. Also, a virtual NIN generated for one company cannot be reused again.
What are the KYC requirements in Nigeria?
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) issued a Supervisory Framework for Payment Service Banks in 2021 that aims to protect consumers and streamline their operations in a transparent manner. These guidelines emphasise the usage of mobile and digital solutions to enhance access to financial services in the country.
The framework also makes it necessary for financial institutions to comply with the Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) regulations, to ensure that their firms are not being used in money laundering or financing terrorism.
An important development in the KYC procedure in Nigeria includes a three-tiered system for KYC verification, where customers are classified into three tiers according to their risk values.
1. Tier 1
These customers are subject to less scrutiny by financial institutions since they represent those with a lower risk value. The information required from them includes
- Name
- Place of birth
- Date of birth
- Gender
- Address
- Telephone number
- Passport size photograph
For tier 1 customers, the evidence of information provided by the user or verification of the same is not required.
2. Tier 2
For tier 2 customers, the information and documents required for KYC are the same as that in tier 1.
In addition to this, the information provided by the customer has to be verified against official databases like National Identity Management Commission (NIMC), Independent National Electoral Commission (INEC) Voters Register, and Federal Road Safety Commission (FSRC) among others.
In this case, the basic customer information has to be verified and monitored diligently.
3. Tier 3
The tier 2 customers represent those with the greatest risk, in the case of which financial institutions have to record, verify and maintain all documents provided by the customer, along with adherence to all KYC and AML/CFT requirements.
Screening customers in Nigeria
Once customers’ identity has been verified, the next step is to screen them against sanctions, PEPs and adverse media lists.
1. Monitored lists
This involves screening customers against global and regional lists to uncover sanctioned individuals or any involvement in financial crimes. Some sanctioned lists that uqudo uses are
- International sanction lists (FATF, OFAC, UNSC)
- Regional sanction lists (MENAFATF, EU, GIABA, ESAAMLG)
- Money laundering
- Terrorist financing
- Drug trafficking
- Narcotics trafficking
- Human rights violations
- International treaties violations
2. PEP lists
PEPs (Politically Exposed Persons) are those individuals who hold a prominent position at a political level, or in large international organisations. Their influence over numerous people/bodies categorises them as high-risk individuals.
Identifying and monitoring PEPs is a key step in a company’s screening process.
3. Adverse Media Screening
Another important screening process includes checking customers against adverse news articles, to find out if they have been involved in financial crimes in the past, or are associated with financial criminals.
While verifying customer details during KYC, lower-tiered users are subject to standard due diligence procedures, while high-risk customers require enhanced due diligence.
The Nigerian Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) is the organisation responsible for analysing the information submitted by financial institutions regarding their anti-money laundering initiatives.
The standard steps for screening involve the assessment of high-risk individuals, including
- PEPs, which refer to those individuals holding a prominent public position or are closely associated with someone who does.
- Individuals in sanctioned lists.
- Individuals from high-risk countries that currently feature on global sanction lists.
- Individuals who have a past history of financial crimes, or are currently facing proceedings.
- Individuals who feature in numerous adverse media articles.
- Individuals who perform unusual high-valued transactions.
These high-risk individuals mandate a stricter KYC and screening procedure, in order to protect financial institutions from fraud, money laundering and terrorist financing.
Financial institutions that don’t comply with KYC and AML/CFT regulations are subject to hefty fines, and imprisonment in some cases.
Authentication of users in Nigeria
For authenticating users, numerous methods can be used like;
1. Passwordless login services
This can help users log in using biometrics, push notifications, OTPs etc for a formless and quick passwordless authentication.
2. Biometric authentication
This lets users sign in using biometrics, which includes their facial features, fingerprint or iris recognition, being more convenient without the hassle of remembering passwords.
3. Two-factor authentication
Adding a second layer of security, 2FA lets users use two different authentication methods, to protect their sensitive information.
4. FIDO & FIDO2 authentication
This is a passwordless authentication method, that lets users sign in with pass-keys from their local devices, eliminating the need for passwords.
How can uqudo help you onboard users efficiently in Nigeria?
uqudo has partnered with numerous financial institutions in Nigeria, including GetEquity to provide a seamless KYC and onboarding experience.
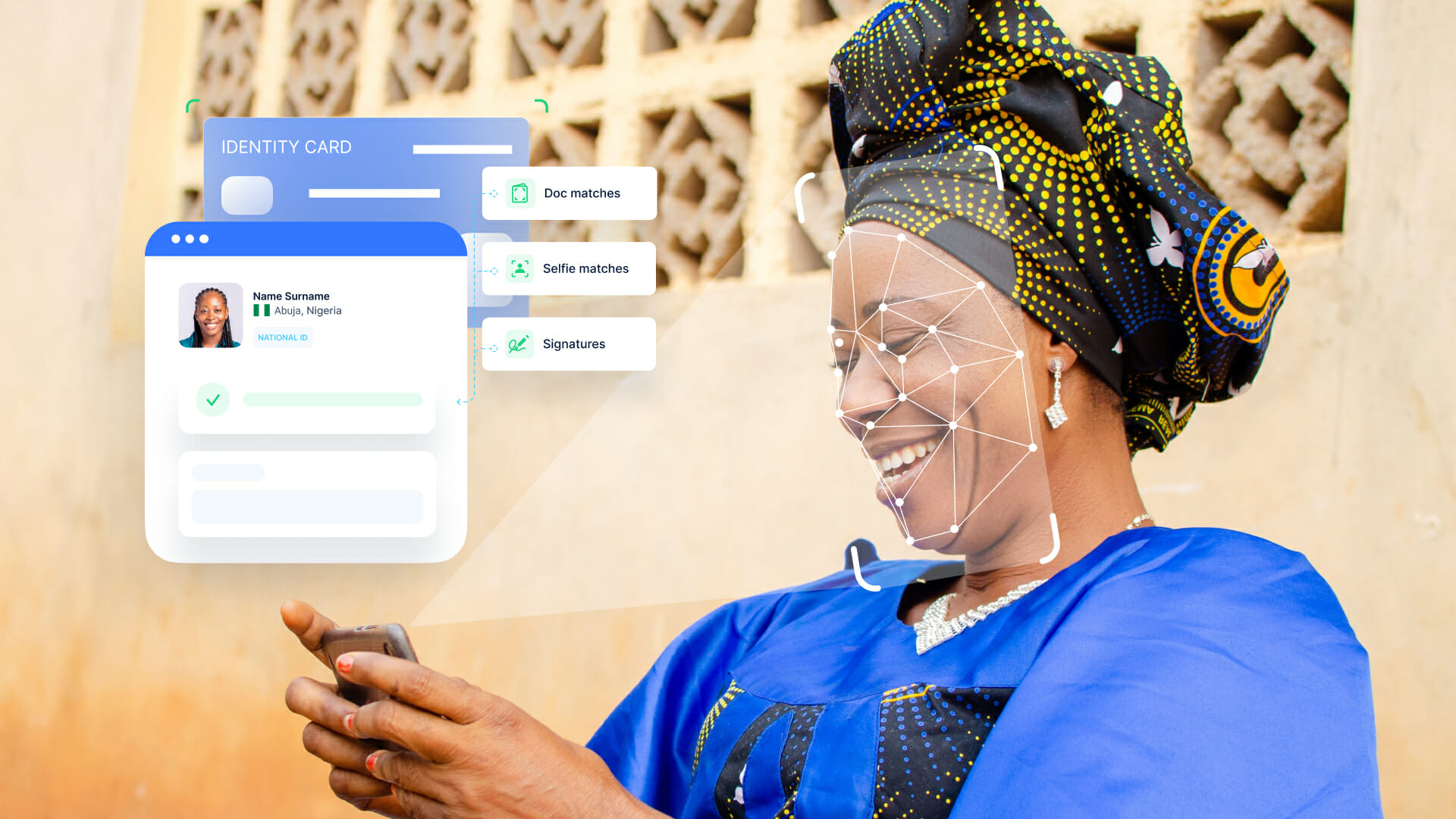
1. Step 1 – AI Document Scanning + OCR
a. Use our powerful AI document scanner to quickly read and scan identity documents, including
-
- Passports
- ID cards
- Driving Licenses
b. Evaluate the quality of the document, and also check for tamper.
c. Identify necessary fields on the document, and extract data using Optical Character Recognition.
2. Step 2 – Face Verification and Liveness Detection
a. Verify if the user on the camera is real, and matches the document.
b. Detect if the person on the camera is live and not a spoof.
3. Step 3 – Identity verification
Once a user is identified, access government repositories to verify their identities.
4. Step 4 – Screening
Check if the individual is worth doing business with, using AML, sanction, PEP and adverse media screening.
5. Step 5 – Passwordless login
Once a user has been onboarded, let them log in to your platform in a hassle-free manner using biometrics or FIDO2 authentication.
Enhance your user onboarding in Nigeria by letting uqudo perform all the necessary checks and evaluations, keeping you compliant with regulations and protected from financial crimes. Get in touch with us to learn more!