Picture this: A bank processes thousands of new account applications daily while monitoring for potential fraud. Simultaneously, an e-commerce marketplace verifies seller identities to protect buyers from counterfeit products. Across town, a telecommunications provider validates customer information to comply with SIM registration regulations. What invisible thread connects these diverse scenarios? The critical need is to know who stands on the other side of each transaction.
In our hyperconnected world, where digital interactions have largely replaced face-to-face meetings, financial institutions, online marketplaces, and telecom companies face an unprecedented challenge: establishing unshakeable trust without physical presence. Document verification has emerged as the cornerstone of this new trust architecture, transforming how these industries validate identities while navigating increasingly sophisticated fraud attempts.
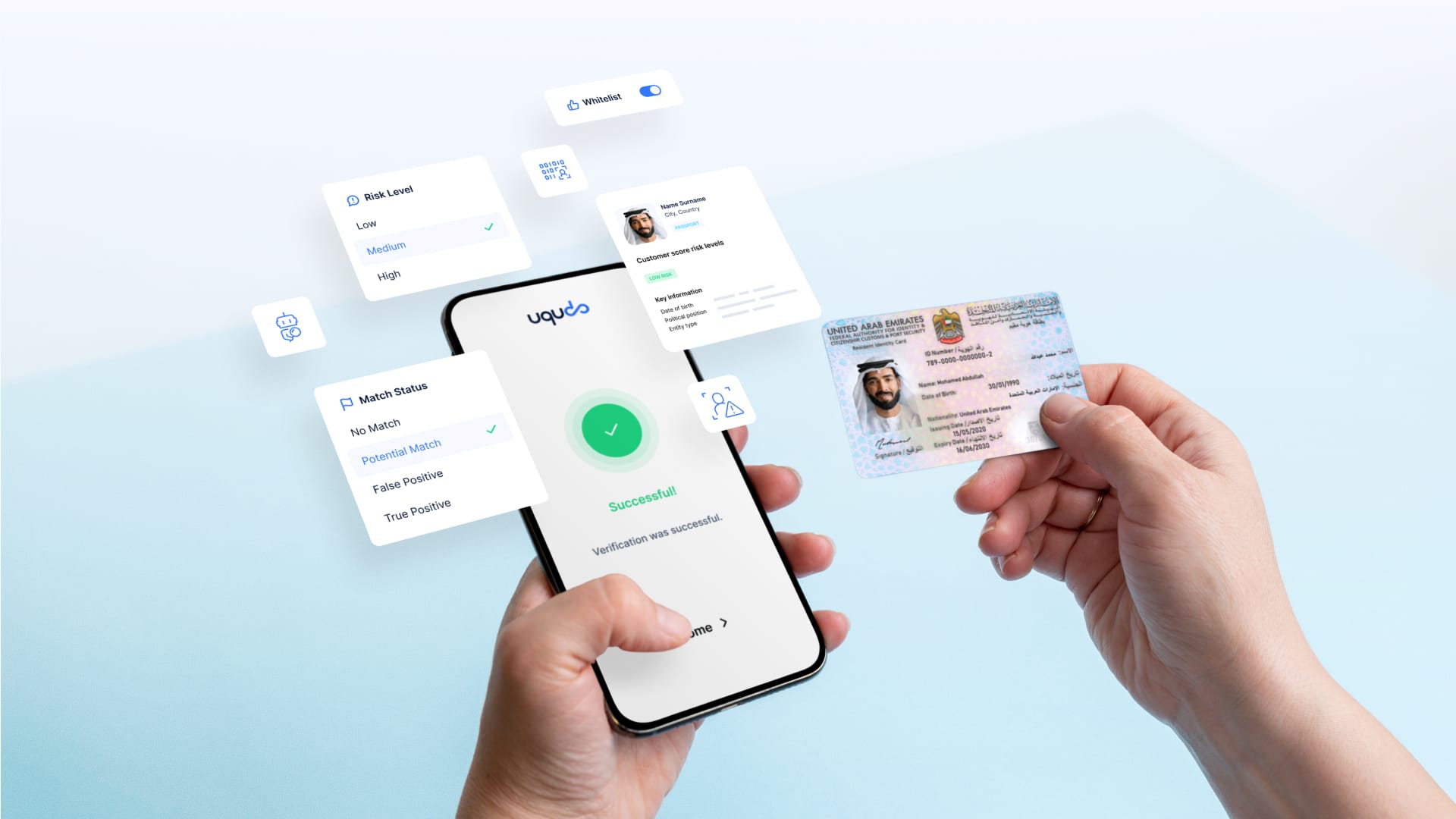
What is Document Verification?
Document verification is the systematic process of confirming the authenticity and validity of identity credentials such as passports, driver’s licenses, and national ID cards. Unlike simple password checks, this multi-layered approach examines the physical and digital attributes of documents to ensure they haven’t been tampered with and truly belong to the person presenting them.
At its core, document verification serves as the cornerstone of modern identity assurance by confirming that:
- The document is genuine and government-issued
- All security features are intact and unaltered
- The information matches across all data points
- The document rightfully belongs to the presenter
Modern verification solutions leverage sophisticated technologies to transform what was once a manual, time-consuming task into a seamless digital process that takes just seconds to complete.
How Does Document Verification Work?
Modern document verification follows a comprehensive five-pillar process flow that scrutinizes identity documents across origin, integrity, coherence, presence, and user behavior:
1. Source Detection
This first line of defense determines a document’s authenticity by understanding its source:
- Screen Detection: Identifies if a document is being presented on a digital screen rather than physically
- Print Detection: Analyzes ink patterns, resolution, and paper artifacts to confirm physical properties
- Physical Verification: Assesses texture, reflections, and micro-details that validate genuine government-issued IDs
This critical initial step filters out non-physical documents, which have a significantly higher risk of digital manipulation through image editors or AI tools.
2. ID Photo Integrity Check
Every pixel undergoes forensic-level scrutiny to ensure the document remains unaltered:
- Image Analysis: Examines overall quality, resolution, and color profiles
- Metadata Examination: Reviews embedded digital information for inconsistencies
- Comparison with Original: Matches against reference templates of authentic documents
- Edge Irregularities Detection: Identifies unnatural transitions that may indicate tampering
- Blending Artifact Analysis: Spot areas where manipulation might have occurred
3. NFC Document Present Check
For documents with embedded chips, this step confirms authenticity through cryptographic validation:
- NFC Reading: Extracts data securely from the document’s chip
- NFC Verification: Validates cryptographic signatures that are nearly impossible to forge
- Physical Assurance: Short-range technology (approximately 10 cm) ensures the document must be physically present
4. Consistency Check
Cross-validation examines multiple data sources to confirm they tell a coherent story:
- MRZ Data: Validates Machine Readable Zone format, checksums, and information
- OCR Data: Confirms text extracted from the document matches other data fields
- NFC Data: Compares chip data with visible document information
- Holistic Discrepancy Alerts: Flags mismatches such as birthdates differing between fields
- Barcode Reading: Translates barcode data for comparison with other document elements
5. Event Analytics-Based Detection
This final layer examines user behavior during the verification process:
- Document Scanning Failed Attempts Analysis: Assesses frequency and patterns of verification failures
- Risk Scoring: Higher numbers of failure messages correlate with elevated fraud risk
The entire verification flow typically completes in under 30 seconds, providing near-instantaneous results while maintaining exceptional accuracy.
Why Do We Need Document Verification?
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the Middle East and Africa identity verification market is projected to reach USD 1,828.77 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 12.20%. This remarkable growth underscores the increasing necessity of robust verification systems.
Rising Fraud Rates
Identity fraud has reached unprecedented levels globally, with recent industry reports highlighting alarming increases in fake identification documents across developing countries. As fraudsters adopt increasingly sophisticated techniques, including AI-generated forgeries and deepfakes, traditional verification methods have become inadequate for detecting these advanced deception attempts. This evolution of fraud tactics requires equally evolved countermeasures to protect organizations and their customers.
Regulatory Compliance
Financial institutions and businesses navigate complex KYC and AML frameworks across the MENA region, with each jurisdiction enforcing unique standards. Document verification establishes the foundation for compliance programs. Direct connections to government identity databases allow for real-time validation of document information against official records. This integration provides ultimate verification, confirming the document matches what’s on file with issuing authorities. These capabilities enable organizations to satisfy regulatory requirements in markets like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Egypt while balancing operational efficiency with thorough identity validation processes.
Tools for Document Verification
Advanced verification platforms leverage several key technologies to ensure comprehensive document analysis:
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
OCR technology automatically extracts text from document images, converting it into machine-readable data. Modern AI-powered OCR systems can accurately capture complex data across multiple languages and document formats, including Arabic script that poses challenges for generic solutions.
Machine Readable Zone (MRZ)
MRZ technology specializes in decoding the standardized alphanumeric code found on passports, visas, and identity cards. This specialized scanning capability processes the structured data format containing critical information like document number, birth date, expiration date, and nationality. Modern MRZ readers achieve over 99.5% accuracy and can detect fraudulent alterations by validating checksums and cross-referencing internal data consistency. The technology functions reliably across challenging lighting conditions and various document orientations, making it essential for border security and KYC processes.
NFC Technology
Near Field Communication (NFC) enables contactless verification of electronic documents like biometric passports. By reading the secure chip embedded in these documents, NFC verification provides the highest level of assurance as the encrypted data is virtually impossible to forge. NFC readers only work for distances of approximately 10 cm, making verification highly secure.
Pattern Recognition
Advanced algorithms analyze documents for expected security features such as holograms, microprinting, and specialized inks. These systems learn to identify subtle inconsistencies that might indicate tampering or forgery that would be invisible to the human eye.
Tampering Detection
Advanced algorithms scan document images for manipulation evidence. The system meticulously examines pixels to detect digital artifacts indicating image editing software was used. This technology identifies suspicious inconsistencies in color patterns, compression artifacts, edge integrity, and metadata that standard verification might miss.
Document Verification Use Cases
Document verification has become essential across numerous industries:
Banking and Financial Services
Financial institutions implement document verification to comply with KYC regulations, prevent fraud, and enable secure remote account opening. This technology allows banks to confidently verify customer identities for account openings, loan applications, and high-value transactions without requiring branch visits.
E-commerce and Marketplaces
Online platforms deploy document verification to build trust between buyers and sellers, particularly for high-value transactions. By verifying marketplace participants, these businesses can significantly reduce the risk of fraudulent activities and chargebacks.
Telecommunications
Telecom companies implement document verification to comply with SIM registration regulations and prevent subscription fraud. By verifying customer identities during the onboarding process, carriers can reduce their exposure to fraudulent activities like SIM swapping.
Selecting the Right Document Verification Solution
When evaluating document verification providers, organizations should consider:
- Global Document Coverage: Ensure The solution must support identity documents from all relevant global regions, including validation of over 13,000 different NFC-chipped passports with their various versions. Comprehensive coverage ensures businesses can verify users worldwide while maintaining regional compliance requirements.
- Technology Integration: Look for comprehensive capabilities including OCR verification, NFC, biometric matching, and tampering detection.
- Accuracy Rates: Assess the provider’s false positive and false negative rates to ensure reliable results.
- Speed and User Experience: Consider verification completion times and the simplicity of the user interface.
- Compliance Standards: Verify that the solution meets relevant regulatory requirements in your jurisdiction.
- Security Certifications: Check for robust data protection measures and industry certifications.
- Scalability: Ensure the system can handle your verification volume, especially during peak periods.
- Support and Expertise: Evaluate the provider’s understanding of local regulations and their customer service capabilities.
Looking Forward
As we navigate an increasingly digital world, document verification will continue to evolve alongside emerging technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence is already enhancing detection capabilities.
Organizations that implement robust document verification systems today are not only protecting themselves and their customers from current threats but are also laying the foundation for trusted digital interactions in the future.
In a landscape where digital trust is currency, document verification isn’t just a security measure, it’s a competitive advantage that enables businesses to move with confidence in an uncertain world.
Ready to enhance your organization’s identity verification capabilities? uqudo seamlessly provides cutting-edge AI document scanning and digital document verification solutions that combine NFC verification with advanced OCR services to create a seamless yet highly secure verification experience.